24 Hours of Daytona (also. Daytona 24h) is one of the most interesting and popular daily races. Traditionally takes place at the Daytona International Speedway, Daytona Beach, Florida. 24 Hours Daytona takes place on the last weekend of January or the first weekend of February, making it the first major race of the year. Since 1991, the main sponsor of the competition has been the Swiss company Rolex, whose watches are received by all winners, and the race has received the second name 24 Rolex Daytona. Previous title sponsors include Sun Trust and Pepsi.
BEGINING AND GENERAL INFORMATION ABOUT 24 HOURS OF DAYTONA
The racing track was finally completed in 1962. It hosted a three-hour race of sports cars. For the first time at Dayton, Dan Gurney won in a Lotus 19 with a 2.7 liter engine. The main rivals turned out to be several Porsches with non-competitive 1.6 liter engines. Since 1964, the format of the competition has changed. Daytona became a 1,220-mile (2,000 km) race. The full 24 Hours of Daytona covered a distance approximately equal to the 12 Hours of Sebring also held in Florida. In 1966, the format that has survived to this day was approved, and the race received its current name. She made many cars famous, and the Porsche 962c became a legend.

As in other competitions of this type, the task of each team is to cover the greatest distance in 24 hours. Unlike the equally popular races at Le Mans, the 24 Hours of Daytona race is located within the circuit. Since the race is held in winter, one has to take into account that a most part of it takes place at night. Therefore, the organizers made lighting along the track.

To be classified in the 24 Hours of Daytona, a car must reach the finish line on its own. In order to avoid disqualification, many teams resorted to trickery and lined up in the pit lane waiting for the time when it would be possible to finish the race in the general classification.
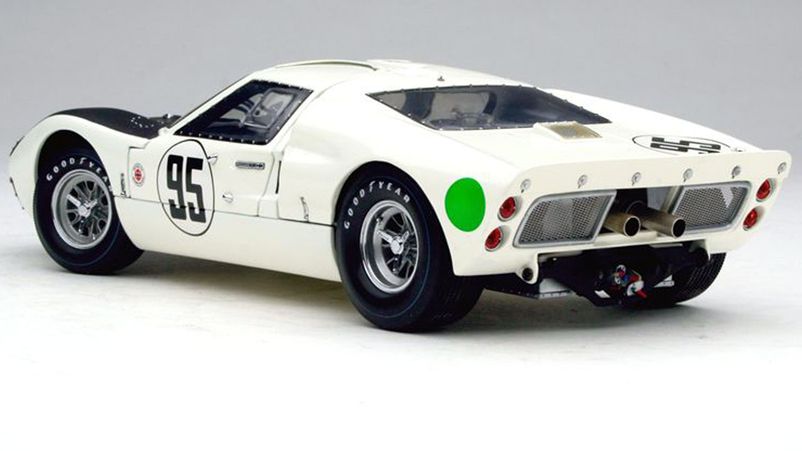

Ford's dominance in 1966 was interrupted by the Italians from Ferrari, who in 1967 occupied the entire podium. Winning the GT class was so important to the Italian sports car manufacturer that a model called the Ferrari Daytona was released. Victories in other classes remained with Porsche and Ford.
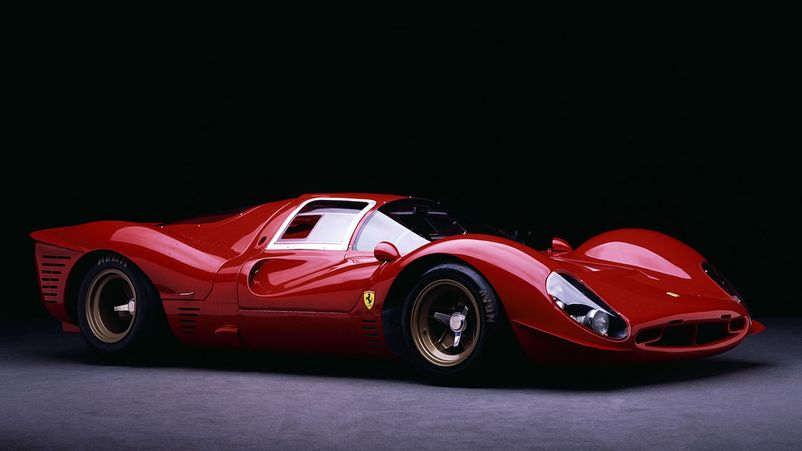

Since 1968, the Porsche era began, which had the largest number of victories. The crisis of 1972 led to the fact that the race was held for 6 hours, and in 1974 did not take place at all. During this period, it was decided that the team should consist of three pilots (today the number can be increased). Since 1982, the 24 Hours of Daytona race has broken away from the European Series (ELMS), which abandoned the American stages, and joined the IMSA GT. In the 90s, the 24 Hours of Dayton moved into the Grand American Series (Grand American Road Racing Association), working closely with NASCAR. In 2002, a new regulation was put forward to save teams money by using less expensive materials. This simplified aerodynamics and resulted in lower training costs. From now on, Daytona is a race available to more people.
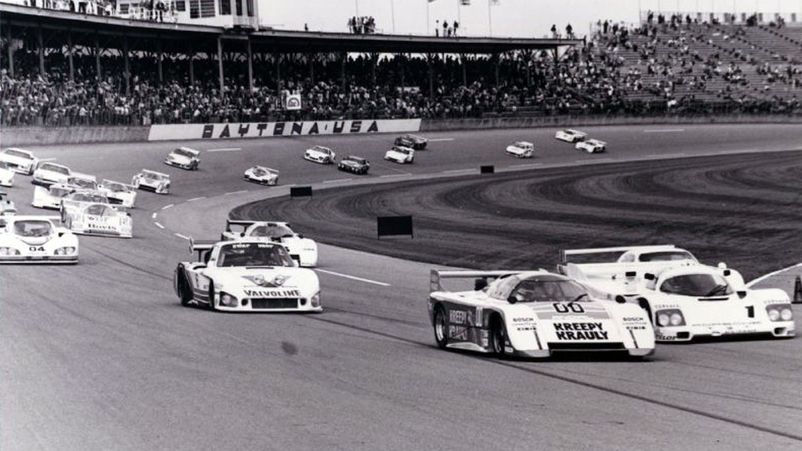

FEATURES AND RULES OF THE 24 HOURS OF DAYTONA RACE
According to the rules, the race must continue for 24 hours. This forces teams to constantly balance between speed and reliability. Cars need to drive the maximum distance during the day (today it is more than 4000 km). The team must have at least three pilots, often more. In the 1962 race, a curious incident occurred when the Lotus pilot - after an engine failure, parked at the finish line, and before the end of the time drove the last meters and became the winner.
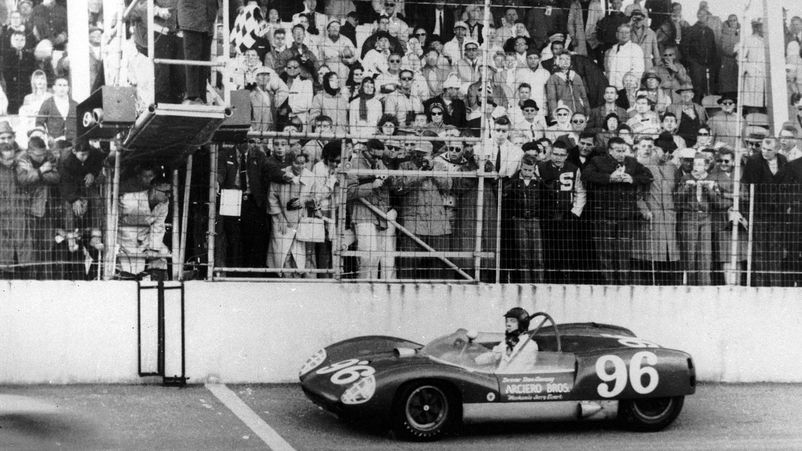

On the track converge in the struggle cars of the European and American series. Competing in the 24 Hours of Daytona are prototypes and close-to-production models in the GT class. A characteristic feature is the absence of a limit on the number of tire replacements. At the same time, prototypes must use tires from Continental, touring versions of the GT - exclusively Michelin. The rules prohibit the use of heating pads and after leaving the pilot spends time warming up the tires. The pit lane located in the infield (the inner part of the circuit) is separated from the main track only by a small lawn, which poses a certain danger to mechanics working during pit stops. The pits are separated by a concrete barrier that the rider is forced to jump over during the driver changeover. For repairs, cars are called to a special area located inside the oval.

ROUTE
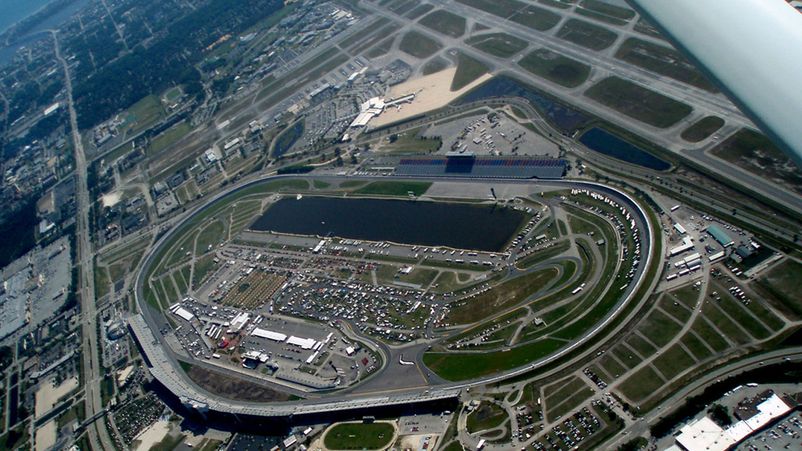
Built in 1959, the Daytona International Speedway has become one of the fastest in the world. The angle of elevation on turns (banking) reaches 31 degrees, providing a ten-meter vertical drop for passing them at high speed. This configuration provides an excellent view from the track's 100,000-strong stands.
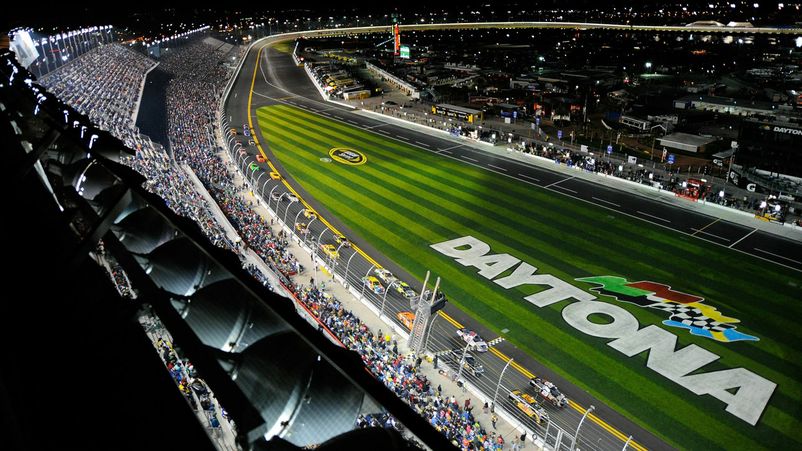

The 24 Hours of Daytona do not run along the classic oval. Within its limits there are separate elements of the route with turns and chicanes. The lap distance is 5.728 km (3.56 miles). The last time it was reconstructed in 2003 (in the inner part, the turn was removed, which slowed down the movement too much). The race takes place in winter, when the night lengthens and the lights turn on by 20% so that cars can drive under their own headlights.

24 HOURS OF DAYTONA RACING SERIES COMPOSITION
The race is included in the World Sportscar Championship IMSA GT Championship (Grand Am) which appeared in 2000. The management of 24 Hours of Daytona tries not to exceed the costs of technology and materials, thereby equalizing the opportunities for teams and increasing interest in the race. Unlike similar races in the series, there are European prototypes here, which makes it more popular.
CARS
The racing series includes 4 classes:
AMERICAN PROTOTYPES
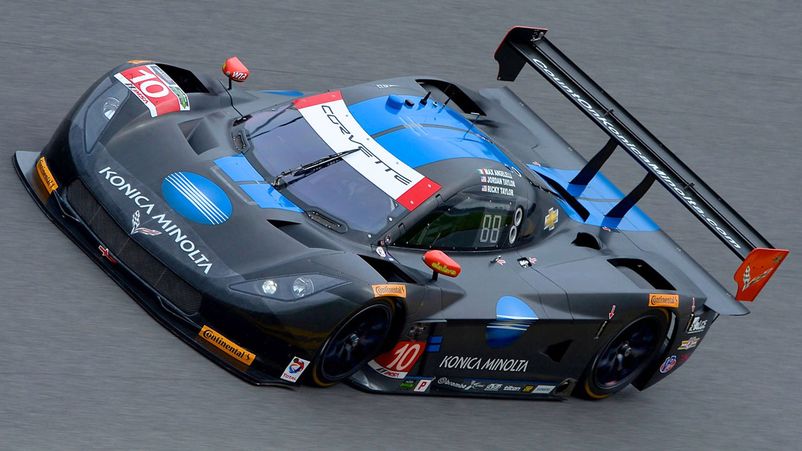
"Daytona Prototype" is equipped with powerful engines with large volumes (over 5 liters). The engine of well-known manufacturers - Chevrolet, Ford, BMW and the chassis of Riley, Fabcar, Doran companies is installed on the tubular frame. With high power (650 hp), cars are not agile enough, especially in corners and chicanes.

LMP2 VERSIONS
Also specially prepared for the race. The maximum speed on the straights is higher than LMP1.
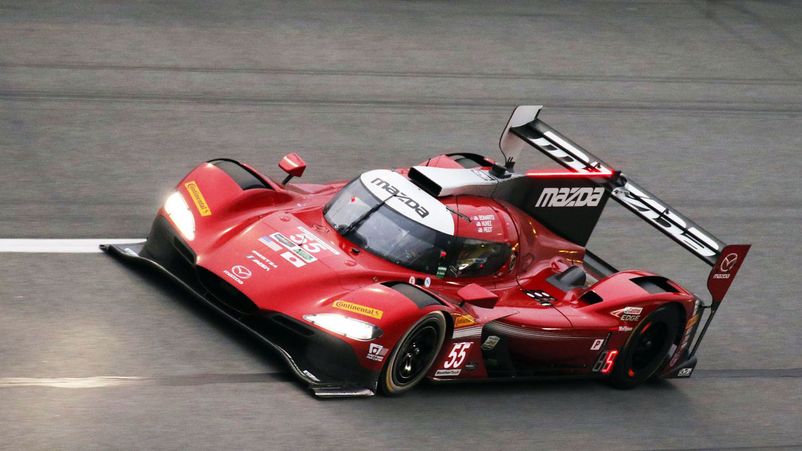

PROTOTYPE CHALLENGE
Prototype Challenge (PC) - a separate class reminiscent of the European LMP2 (open cockpit). Cars are equipped with engines from Chevrolet on the Oreca chassis. The maximum power is 430 hp. Amateurs can compete on such fireballs.
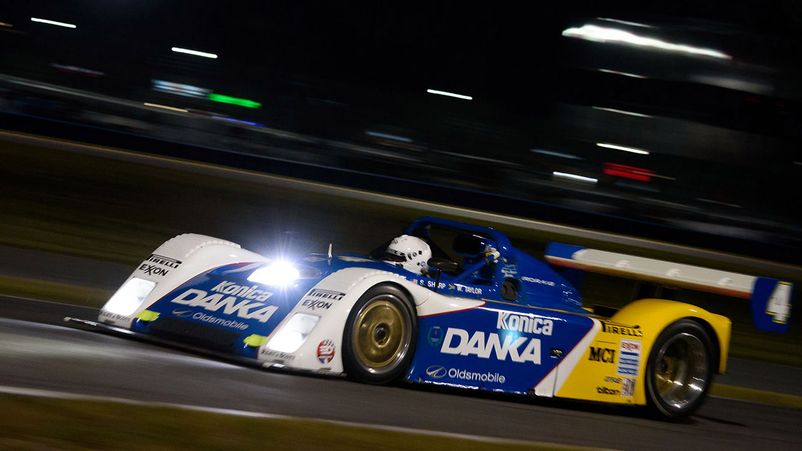

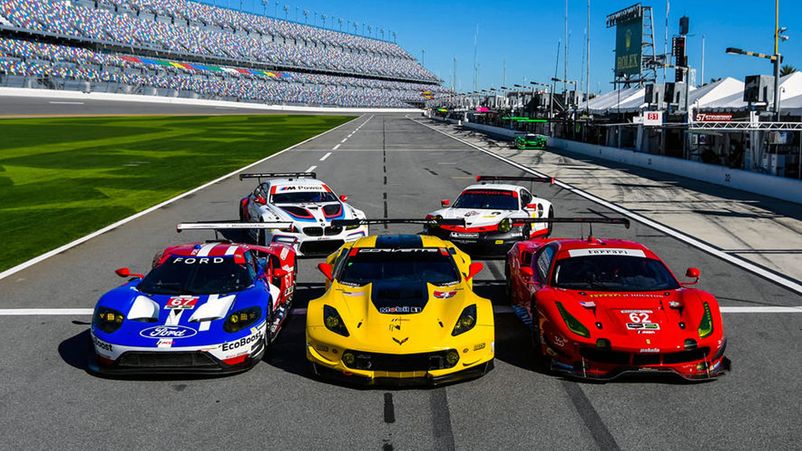
GRAN TURISMO, GT3 AND GX
Body class with clear regulations and an engine capacity of more than 2 liters. They are similar to production cars, have less power compared to prototypes. The maximum possible indicator is 490 hp. Traditionally participating in the 24 Hours of Daytona are: BMW, Porsche, Chevrolet, Ferrari, Ford, Dodge. GT Daytona - represented by GT3 models. There are traditionally many participants in this class. Power is limited to 450 hp. Amateurs can perform. In 2013, the GX class was introduced, which unsuccessfully entered the diesel Mazda 6.

FAMOUS RIDERS AT 24 HOURS OF DAYTONA
Another distinguishing feature of 24 Hours of Daytona is that the race is held in the off-season of other world-famous racing events. Famous riders from different series often compete in the race. At various times at the "24 Rolex Daytona" were:
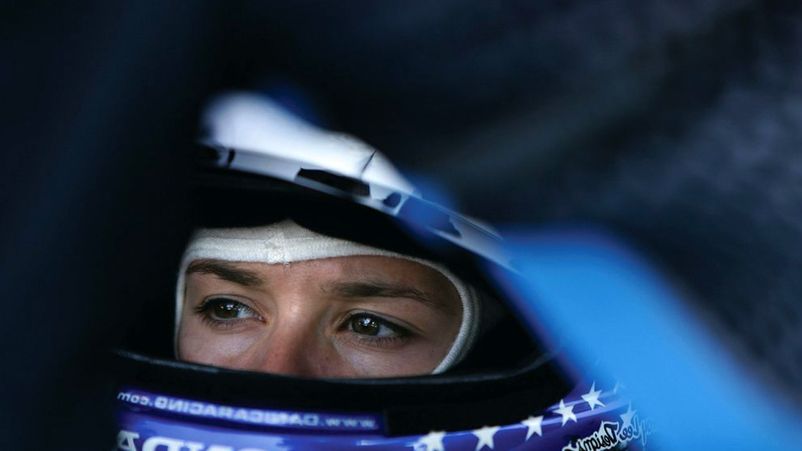
- Danica Patrick is a famous NASCAR racing driver. In 2005, she became IndyCar and Indy 500 Rookie of the Year. Danica was close to signing a contract with the Formula 1 team, but the deal fell through.

- Jimmie Johnson is a seven-time NASCAR Series winner. Taking part in the Grand-Am series, which includes the 24 Hours of Daytona, he was in the top ten in 7 out of 9 races.

- Greg Biffle is a racing driver from the USA. Champion and vice-champion of NASCAR. Known for its sporting spirit.

- Paul Tracy is a Canadian driver who won Champ Car 2003. Nine has focused on marathon races such as Daytona, Sebring and Le Mans.

- Sebastien Bourdais is a French racing driver. Won four times in Champ Car and once in Formula 3000. After a bad experience in Formula 1, he moved to endurance racing.





