This international championship series for GT cars class has been held by the FIA since 2004. Most of the races are held at Japanese circuits, but having gained worldwide fame for the sake of popularization, some stages of the series go to other countries.
THE HISTORY OF THE SUPER GT
At the end of the twentieth century, interest in touring car racing in the world grew. Motorsport was on the rise, with the result that various racing championships began to appear, among which was the Super GT. Japan, as one of the world's largest automakers, has become the ancestor of this popular touring car race.

JGTC
In 1993, the Japan prototype Championship changed and the Japan Automobile Federation formed the JGTC through the GT-A organization. To increase the interest of the audience, the power of the motors was limited, and the winners received weight penalties. This increased the intensity of the struggle, reducing the importance of the design advantages of individual models. The first exhibition race, ISMA GT, was mostly attended by JSS (Japan Sport Sedan) and two Racing Nissan Skyline GT-Rs of the JGTC class (such as the Xanavi JGTC Skyline GT-R R34), and the stage was the first in the history of the championship. European brands first appeared at the Suzuki Circuit.

The rules were revised in 1994. Two classes were offered, with FIA requirements - GT1 and GT2. The more numerous JSS subclass went to GT2. JGTC had new opportunities - they could compete with last year's cars or exhibit IMSA GTS prototypes. In the season, prototypes from group C showed themselves (in order to return competition, they were later banned).
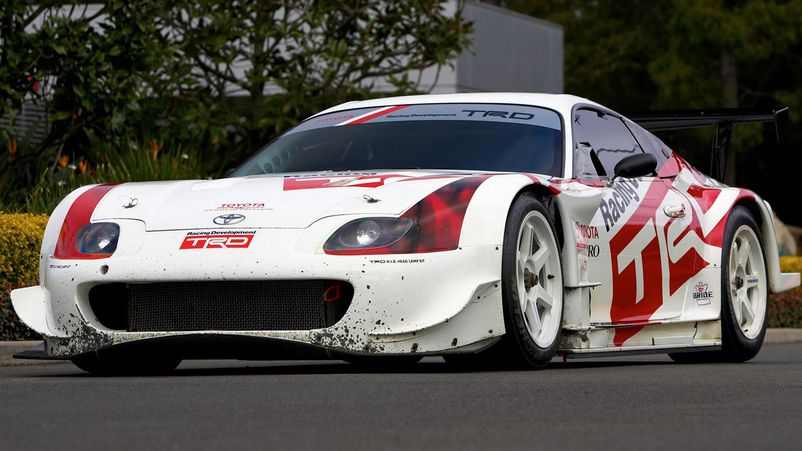

An excessive increase in financial spending resulted in the creation of the GT300 and GT500 subclasses in the 1995 season. They differed in mass and power, regulated by an air restrictor. Two-door models have been allowed since 2002, with the only exception being the Cusco Racing Subaru Impreza. Gradually, the championship began to reach a new level, a stage was held at Sepang in Malaysia. To increase popularity, stages were later held in Shanghai and California. This experience was unsuccessful and they were abandoned.
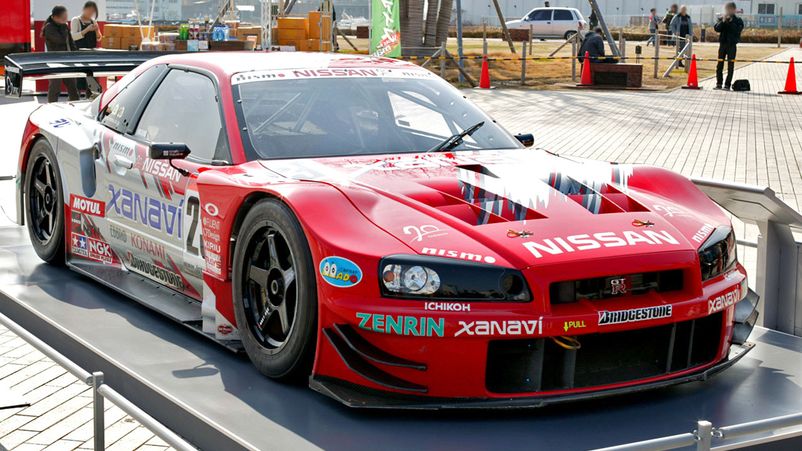

Birth of the Super GT
Gradually the series outgrew the national level, but attempts to go further caused difficulties due to the restrictions of the FIA. To get around the bans, it was reformatted and on August 10, 2004, a new class appeared - Super GT. In order to become more popular DTM, it was decided to go on international level by holding a non-Japanese stage. The competition came under the leadership of the International Automobile Federation, it was planned to hold other stages outside of Japan.
SPORTING REGULATIONS SUPER GT
The championship is held annually, several of the most famous Japanese tracks are included - Fuji Speedway, Suzuka. Check in is carried out at Sepang in Malaysia. They tried to establish themselves in the USA (the attempt was unsuccessful). The Malaysian stage was the only non-Japanese one.
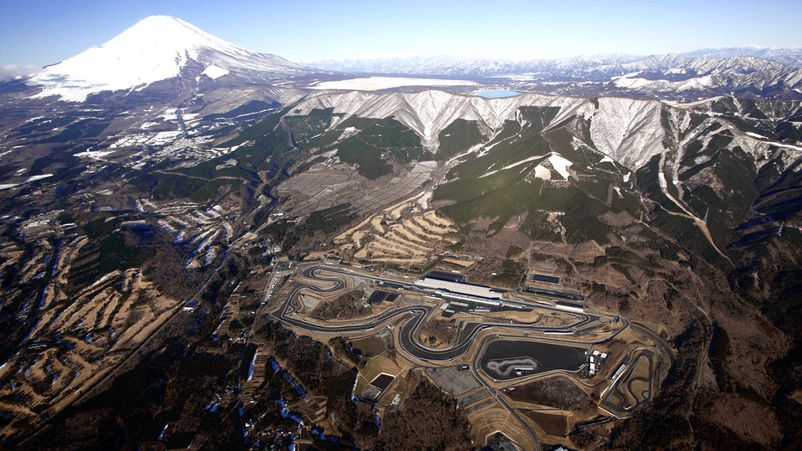

At the Suzuka circuit, there is a long 1000 km race carried our. The race is held simultaneously for both types of cars, with a separate classification of participants.
TECHNIQUE
Class regulations are divided into two parts: GT500 with 500 hp and engine and GT300 with 300 hp, accordingly. Power is regulated by a special intake manifold air intake (restrictor). The diameter of the restrictor depends on the mass of the car: the more weight, the more power is allowed.

On the Super GT, control electronics are completely prohibited: stabilization systems, control systems, ABS. Ceramic brake discs are not used, certain types of rear spoilers and wings are prohibited. Different tires are used, regular partners are Bridgestone, Kumho, Yokohama, Dunlop, Hankook and Michelin.

GT500
The most prestigious racing class, the most successful Japanese brands in it are Honda, Toyota / Lexus and Nissan.
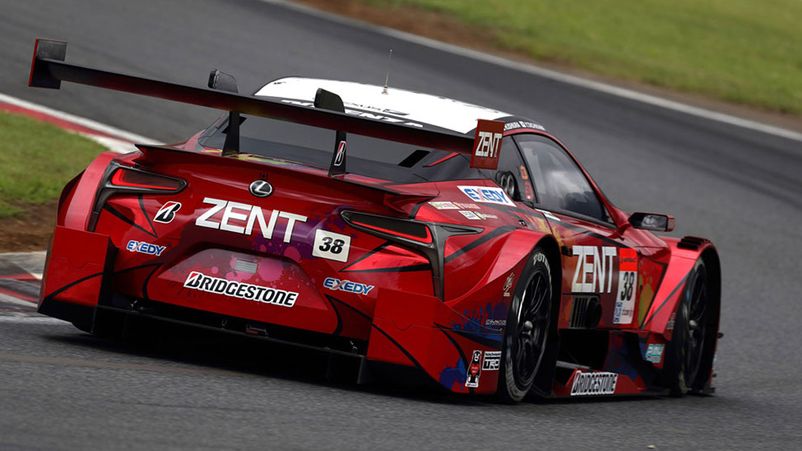

Some also exhibit European brands: Ferrari, Aston Martin, McLaren, Lamborghini.
Loyal rules apply: modified engines are allowed, turbines are allowed also. The body, externally similar to the serial one, can be reinforced with a tubular frame. The refinement of the chassis is practically unlimited. The result is Super GT class cars that are among the fastest in worldwide motorsport. The restrictions do not encourage auto homologation, but some manufacturers are developing their own variants, such as the Honda NSX R-GT.

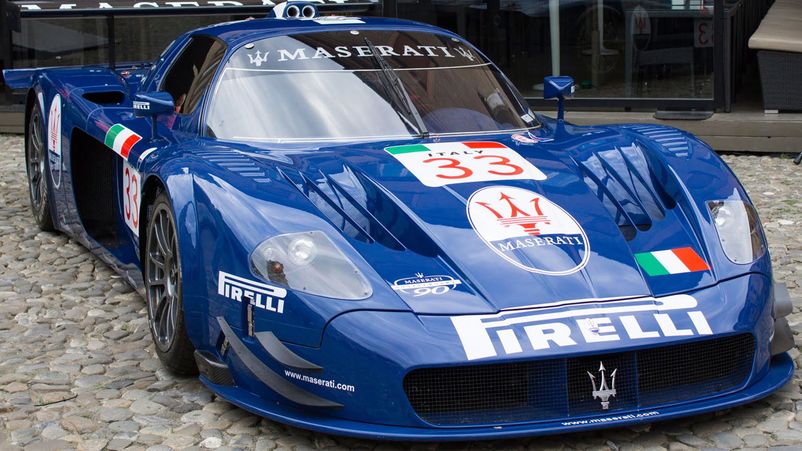
The specifications of the GT1 and GT500 are getting closer and there is a project to gradually merge the regulations to show the same cars. Now SUPER GTs are staying faster due to more liberal aerodynamic requirements. In 2006, one of the best GT1 models, the Maserati MC12, was 1 second slower in Circuit Suzuka corners.

GT300
Far fewer factory teams are interested in this class, but the representation of small manufacturers is large. Starting from 2006, most of the participants compete on European cars and GT3 cars are allowed in SUPER GT from 2010 year.
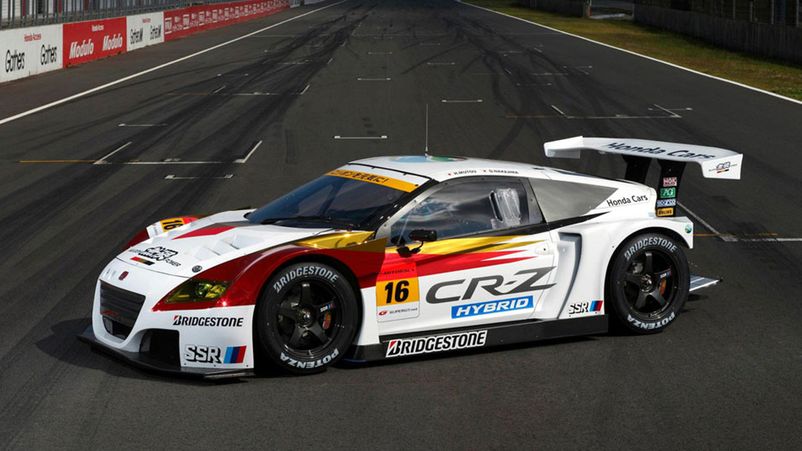

The technical requirements of this class are much stricter, so the cars are closer to serial production. The regulation allows the transfer of the drive from the rear axle to the front.
LEVELING POWER AND THE SUPER GT HANDICAP SYSTEM
Interest in the SUPER GT is due to the system of leveling the capabilities of different cars. Before the season, the car receives a restrictor diameter that limits power. Also, the schedule of mandatory pit stops and a change of pilots is prescribed for each racing stage.
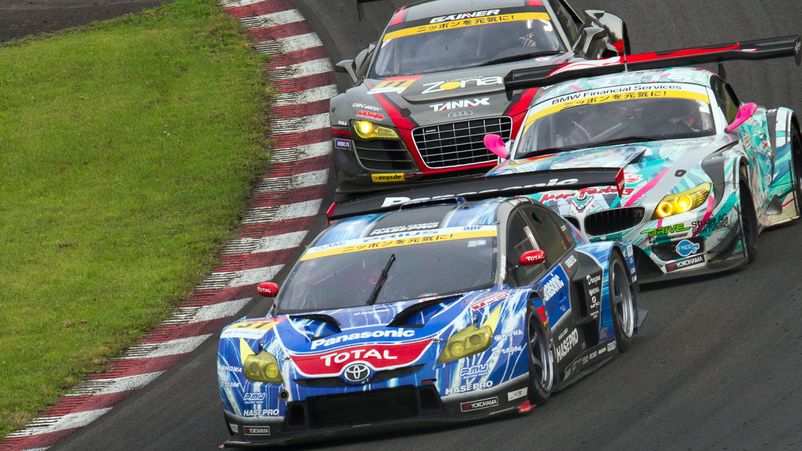

To make the races more interesting, taking into account the results of the qualification and tracking the cars making the fastest laps, a ballast - Handicap - is added to the fastest cars (according to the results of the stage). In 2007, the NSX car presented by Takata out of 7 races won 5 times in qualifying, and won only one. In 2009, a rule was introduced that in the final race, participants who missed no more than one race receive a handicap (ballast).

FAMOUS PILOTS
SUPER GT is the most popular racing series in Japan. Local pilots not only compete, they lead their own teams. The most successful are Hoshino Kazuyoshi, Suzuki Aguri, Hasemi Masahiro.
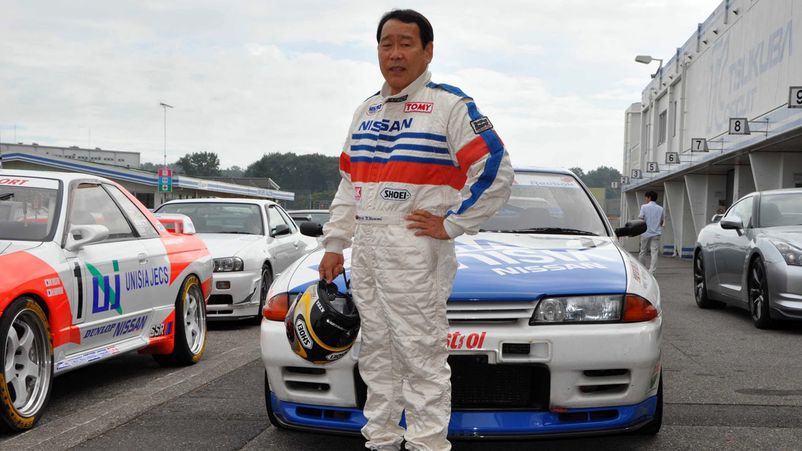

The simplicity of the regulations and high speeds made the championship a forge of young talents, for example, future F1 stars: Ralf Schumacher and Pedro de la Rosa.

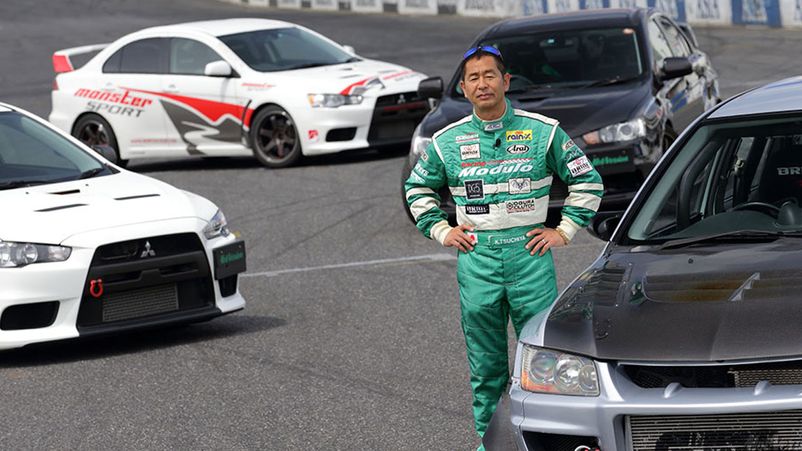
Keiichi Tsuchiya, the Drift King (the unrivaled winner of this type of motorsport) has repeatedly participated in the competition. Interestingly, not only professionals participate in Super GT, well-known actors, singers and TV stars took part in them.

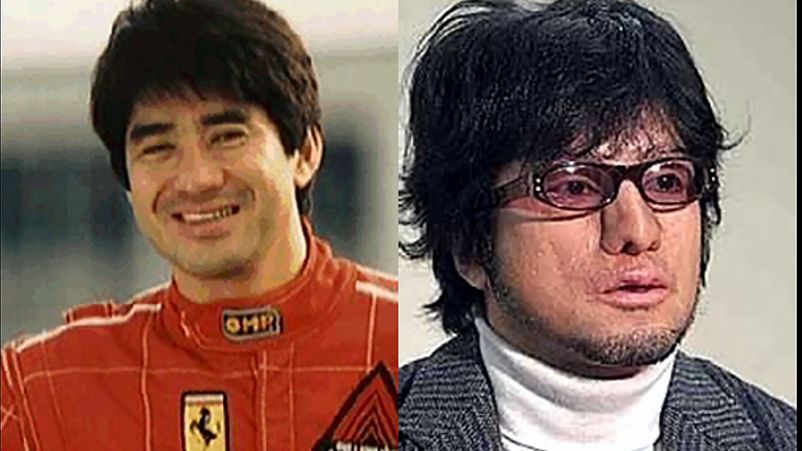
OTA ACCIDENT
The series is not devoid of accidents like any other car racing, but the biggest incident was the accident at the Fuji circuit. The GT300 pilot - Tetsuya Ota on a Ferrari crashed into a Porsche that had previously been in an accident. In the resulting fire, the racer received extensive severe burns.
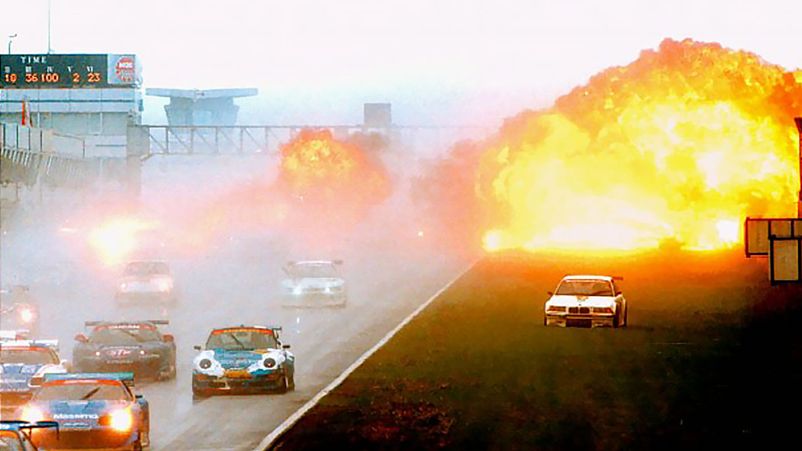

It was proved in court that the accident could have been avoided by picking up the broken Porsche from the track in time. As a result, the organizers paid him 800 thousand dollars.









